

You can download the iris dataset using the following link. Worksheet 172 with answers attached making box and whisker plots Worksheet 173 Answer to Application Problem attached Mathematical Reasoning Test Preparation for the 2014 GED Test Student Book pages 38-39 and 40-47. Let’s load the iris dataset and the necessary packages to begin with. Interpreting a box whisker plot for questions 1 5 refer to the box whisker graph below which shows. The interquartile range is calculated as IQR = Q₃ − Q₁.Īny data points past the whiskers ends are considered as outliers and represented with circles or diamonds. The lower adjacent value is the furthest data point that is within 1.5 times the interquartile range(IQR) of the lower end of the box, and the upper adjacent value is the furthest data that is within 1.5 times the IQR of the upper end of the box. Quartiles are a special case of a type of statistics called quantiles, which are numbers dividing data into quantities of equal size.Įxtending from both the ends of the box plot are called whiskers, which extends till the adjacent values. The Third Quartile(Q3) is the 75 th percentile of the data.
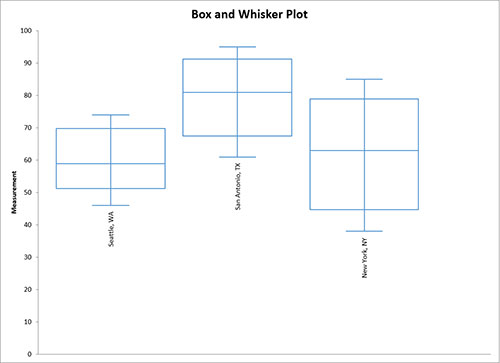

Students use data sets to create or match a box plot. The First Quartile(Q1) is the 25 th percentile value of the data. This math activity provides your students practice in drawing, interpreting, and analyzing box plots (box-and-whisker diagrams). If the median is closer to the top, then the distribution is negatively skewed. The distribution is positively skewed if the median is closer to the bottom. If the median is not in the middle of the box, then the distribution is skewed. Box plots (also called box and whisker charts) provide a great way to visually summarize a dataset, and gain insights into the distribution of the data. The horizontal line represents the median of the data. The box represents two inner quartiles where 50% of the data resides, and it ranges from the first quartile to the third quartile. The first thing you might notice in the preceding diagram is a box that contains a horizontal line. The following diagram represents the box plot. Upon completion of this module, students will be able to use R and RStudio to create. It is created by plotting the five-number summary of the dataset: minimum, first quartile, median, third quartile, and maximum. Video created by for the course 'Managing, Describing, and Analyzing Data'. It is a very convenient way to visualize the spread and skew of the data. Use the plot to find the five number summary, the. The box within the chart displays where around 50 percent of the data points fall. In this video you will learn to interpret a box and whisker plot.TranscriptLets look at this Box and whisker PlotHere is Q1 Q3 the median, the minimum, and.
#Interpreting a box and whisker plot how to
This tutorial shows how to create box plots in Excel. Interpreting Box-and-Whisker Plots After grading his classes exams, a professor summarized the results by using the box-and-whisker plot below. Box and whisker plots portray the distribution of your data, outliers, and the median. The histogram, on the other hand, is an adequate presentation. The data can alternatively be shown using a histogram. Similarly, if a value is lower than the 1.5*IQR below the lower quartile (Q1), the value will be considered an outlier.Box plot, also known as box-and-whisker plot, helps us to study the distribution of the data and to spot the outliers effectively. Box and whisker charts (box plots) are a useful statistical graph type, but they are not offered in Excel's chart types. It is a form of graphical approach that shows how the data in a dataset changes over time. Outlier: If a data point is higher than the 1.5*IQR above the upper quartile (Q3), the value will be considered an outlier. Virtual Nerd's patent-pending tutorial system provides in-context information, hints, and links to supporting tutorials, synchronized with videos, each 3 to 7 minutes long. 11.2 Notes: Interpreting Box and Whisker Plots Name Date Box-and-Whisker Plot A box-and-whisker plot shows the variability of a data set along a. Interquartile range (IQR): It is the box plot showing the middle 50% of scores and can be calculated by subtracting the lower quartile from the upper quartile (e.g. Negatively Skewed: When the median is closer to the upper quartile (Q3) and the whisker is shorter on the upper end of the box, then the distribution is negatively skewed. Positively Skewed: When the median is closer to the lower or bottom quartile (Q1) then the distribution is positively skewed. Normal Distribution or Symmetric Distribution: If a box plot has equal proportions around the median and the whiskers are the same on both sides of the box then the distribution is normal. Step 6: Scale and label an axis that fits the datasets. The max is the largest data point, which is 50. The min is the smallest data point, which is 3.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
